Enhancing CAD Efficiency with AI & ML | Part 1
Customer Experience Journey Mapping
Introduction
Usability-Driven Opportunities
Business Challenge
-
Precision is paramount in the manufacturing sector, requiring careful integration of AI/ML in CAD workflows.
-
Striking a balance is key: users should retain control over results or oversee outputs while reducing manual involvement.
-
AI/ML should focus on repetitive tasks, saving valuable time and improving workflow efficiency.
-
AI/ML models depend on large, high-quality datasets, which are challenging to prepare in CAD for manufacturing.
-
Confidentiality and security concerns are significant when handling sensitive manufacturing data.
My Role
-
I had the opportunity to contribute equally through all stages of the design process.
-
Conducted user research and journey mapping to identify pain points, leading to the discovery of key opportunities.
-
Focused on improving the drawing creation workflow, designing and implementing solutions that enhanced accuracy and reduced turnaround time
Project Overview

UX Designer(3), User Researcher(1), PM(1), CX Director(1)
Team
-
Customer Experience Journey Mapping(CXJ)
-
Research
-
Design
-
Usability Testing
-
Dev Handoff
My Role
6 Months
Duration
Background
In October 2023, Dassault Systèmes' web-based CAD application division set out to expand the possibilities of AI/ML in CAD. The goal was to reduce the time users spent on tasks that AI/ML could handle more efficiently.
While AI/ML had always been a part of CAD, this initiative aimed to reimagine it as a collaborative assistant—a second-person presence helping users complete tasks more effectively, allowing them to focus on areas requiring human expertise.
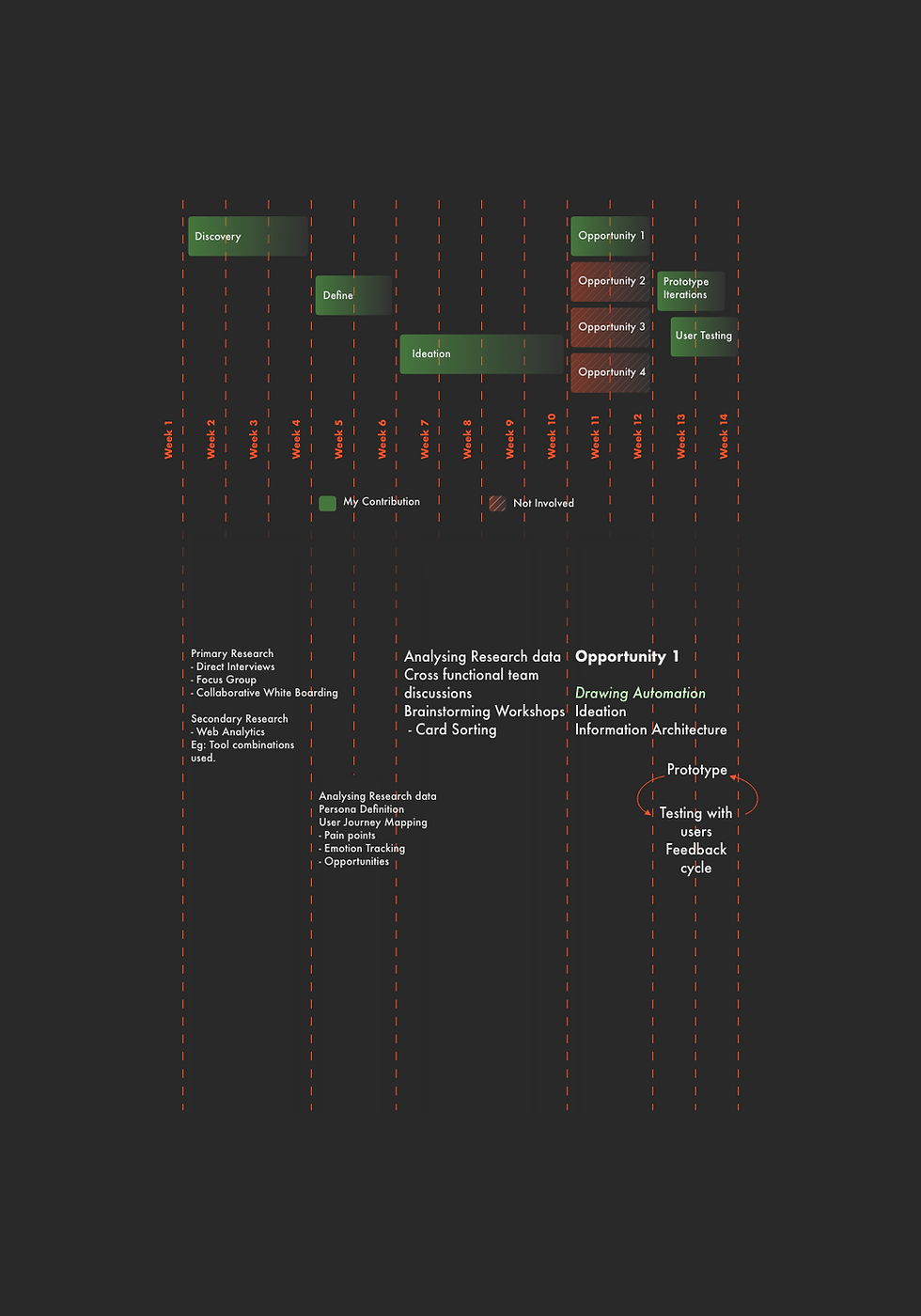

Timeline
Design Evolution Path
-
Discovery Phase: Conducted over 3-4 weeks, connecting with users globally through diverse research methods.
-
Objective: Understand user expectations and concerns regarding AI and ML in CAD workflows.
-
Target Users: Professionals in the manufacturing sector leveraging CAD for precision-driven tasks.
-
Opportunity Identified
-
Integrate AI/ML to enhance CAD modeling by:
-
Automating repetitive tasks.
-
Providing personalized, industry-specific suggestions.
-
Supporting decisions based on manufacturing standards.
-
Expected Benefits: Streamlined workflows, improved efficiency, and enhanced user experience.
-
-
User Testing: Engaged 18-20 participants from various industry domains.
-
Output: Created a user journey map, identifying pain points, opportunities, and emotional touchpoints in CAD workflows.
Discover
User Research
User Demographic + Prep
Solidworks boasts a significant global presence, with 60% of its users located in North America, primarily the United States. It holds a 13.7% world market share, serving diverse user categories including manufacturing, CAD engineers, education, and hobbyists. This widespread adoption underscores Solidworks' prominence and versatility in the CAD software market. 🚀
Before starting, we needed to understand users' expectations and concerns regarding AI/ML. We believed this knowledge would not only guide us in asking relevant questions but also help us establish a hypothesis for the user research.'
Define/CX Journey Mapping/The Map
Generic Journey-Onboarding to CAD System
User persona - 'Type A'
CAD Designer, involved in Initial Design, Detailed Design. Emphasis on drawing creation phase.
-
Key Activities/Touch points
-
Creates design concepts, benchmarks, and finalizes designs.
-
Works on component modeling, material selection, and design validation.
-
Prepares final drawings and annotations.
-
-
Primary Channels:
-
CAD Software: For design, modeling, and drawing.
-
Collaboration Tools for team coordination and feedback.
-
Feedback Systems: Comments on CAD model,(e.g.,Receives input from Shop Floor manager).
-

Key Enablers
.png)
Training Resources
-
Sample projects for hands-on practice.
-
Contextual tooltips and prompts.
-
Searchable FAQs, how-to guides, and troubleshooting articles.

Personalization Features
-
Preference-saving capabilities
-
Configurable tool bars based on user preference/role.
-
Preloaded templates or settings
.png)
Integration with Existing Ecosystems
-
Compatibility with widely used file formats and tools.
-
Support for importing/exporting pre-existing CAD files.
Discover/User Research
Quantitative
Global User Survey
In collaboration with a user researcher, we designed and conducted a global quantitative survey to gain insights into user demographics and expectations regarding the use of AI/ML in CAD workflows.
The primary objective was to understand where users envision AI fitting into their workflows, the type of assistance they prefer, and the extent to which they are comfortable with AI influencing their design processes.
Few questions from the survey (Survey results are not public)
Q. What is your primary role in the CAD design process?
Q. Do you prefer AI assistance that is proactive (makes suggestions) or reactive (responds to specific queries)?
Q. Would you trust an AI model to automate repetitive tasks without manual verification?
Define/CX Journey Mapping/Process
Customer Journey
Mapping Process
To understand user workflows and improve the CAD experience, we conducted a comprehensive customer journey mapping process. This approach provided a clear visualization of user interactions, pain points, and opportunities for improvement, ensuring that our solutions were user-centric and addressed critical challenges effectively.
The process was carried out in three key steps:
-
Validated journey maps through user feedback and usability tests.
-
Refined touchpoints to address overlooked pain points.
-
Identified new opportunities to improve drawing creation workflows.
Step 3: Validating with Real Users and Refining Journey Maps
-
Collected data from user interviews, surveys, and analytics.
-
Created personas for roles like designers, engineers, and managers.
-
Developed end-to-end journey maps to visualize workflows.
-
Identified friction points, especially in drawing creation.
-
Explored pain points and improvement opportunities.
Step 1: Creating Journey Maps Based on User Personas
Step 2: Aligning User Actions, Pain Points, and Emotions
-
Mapped user actions with pain points and emotional responses.
-
Analyzed key phases like tool exploration and output finalization.
-
Conducted collaborative workshops to align on critical challenges.
Dassault Systèmes, 2024
Integrating AI/ML into SolidWorks to streamline workflows, resolve CAD challenges, and enhance user experience.
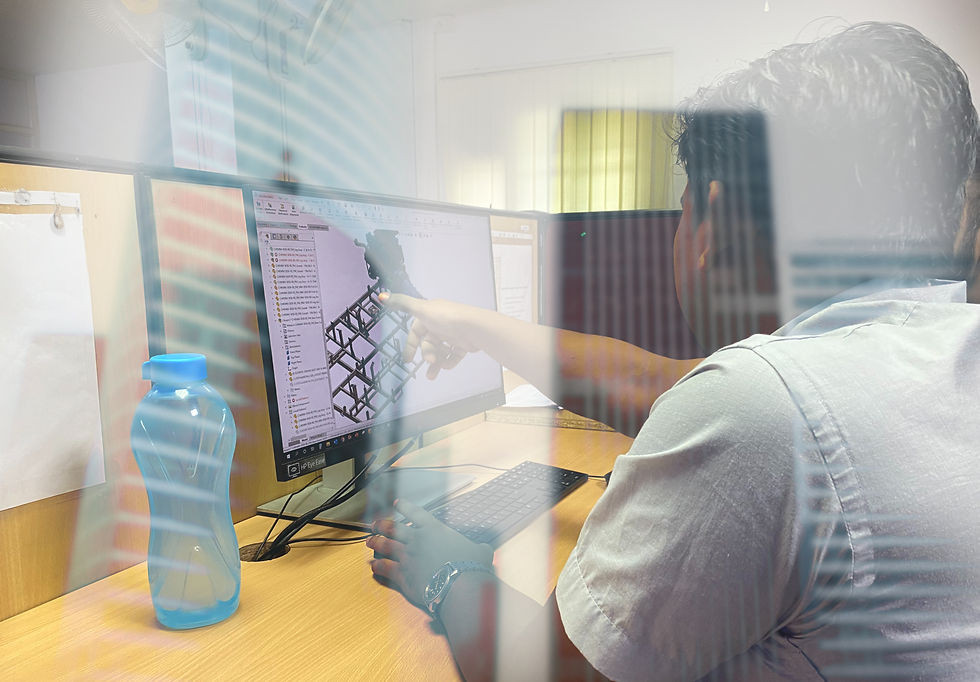

Define/CX Journey Mapping/Workshop
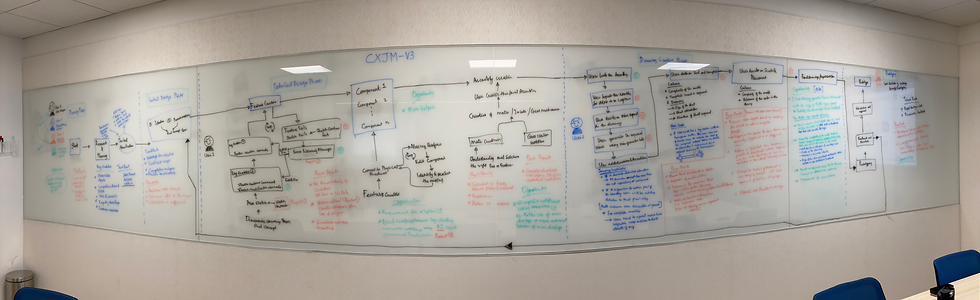
Whiteboards and drawings
We sketched out various customer experience journey maps using whiteboards and sticky notes, covering glass walls to visualize the entire user experience.
It was a collaborative effort—our team worked together, and stakeholders provided feedback directly on the maps, helping us refine and improve them.
Define/CX Journey Mapping/User Personas
Mapping to faces
Design thinking sessions conducted at various stages helped identify key problem statements, which we integrated into user personas. These personas will serve as reference points for understanding user needs, behaviors, and motivations during later stages of ideation and retrospection.

Sara Smith | CAD Designer
Type A
Involved in both Initial and Detailed Design Phases
Sara has 6 years of experience in CAD modeling for manufacturing, specializing in component design and complex assemblies. She’s proficient with CAD tools and enjoys problem-solving but is cautious with AI/ML.
-
Goals: Create high-quality, precise models; streamline repetitive tasks; and incorporate feedback quickly to avoid design delays.
-
Pain Points: Manual adjustments are time-consuming, often gets overloaded with iterations, and experiences limited automation for repetitive tasks.
-
Motivations: Sara is motivated by tools that can enhance productivity, automate redundant tasks, and provide intuitive suggestions. AI-driven modeling tools that predict and adapt to her workflow would be highly valuable.
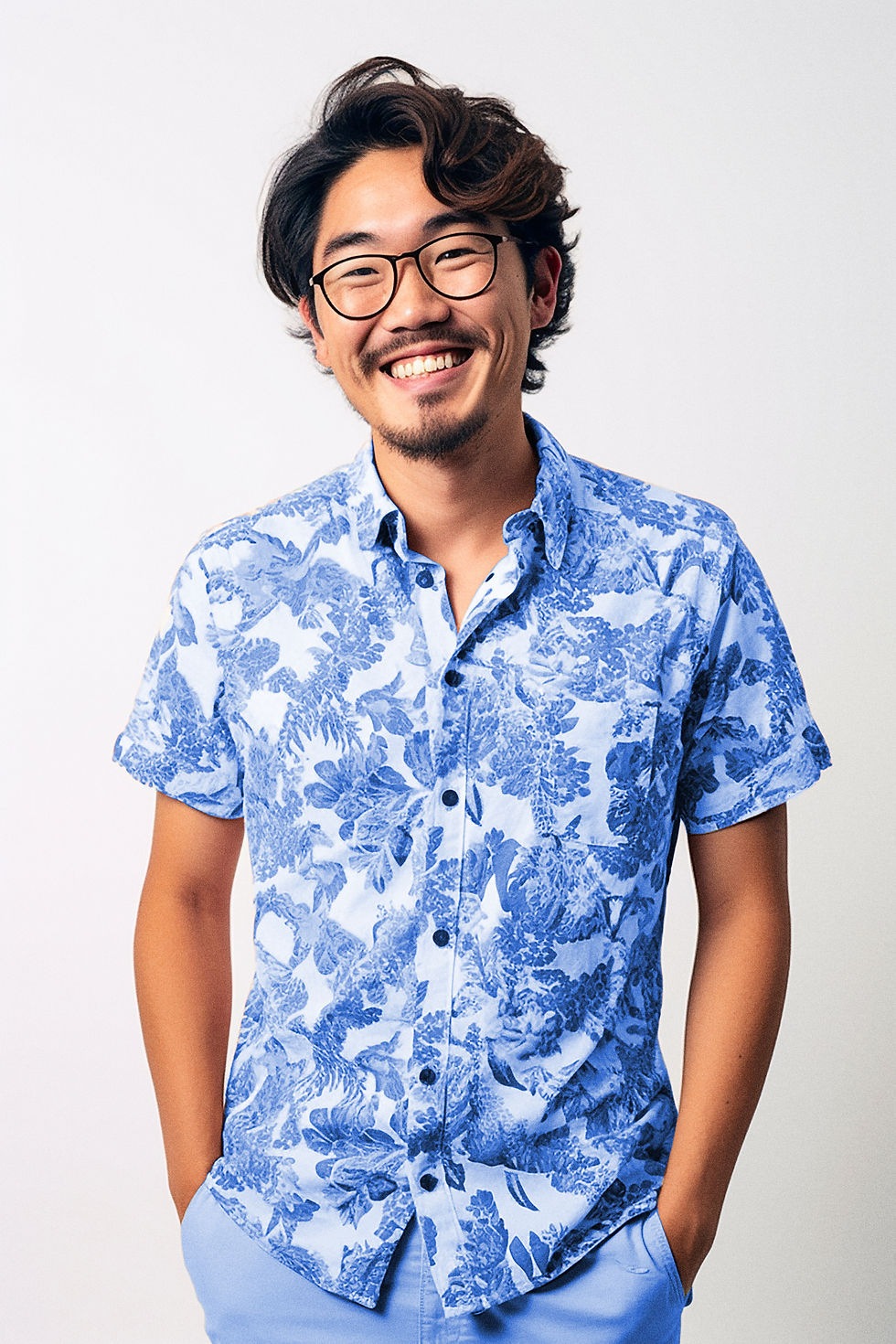

Migom kumb | QA Engineer
Type B
Involved in the Detailed Design, Prototype, and Production Phases
Tim has 10 years of experience in quality assurance, specializing in testing and validating designs before production. His focus is on ensuring design accuracy and compliance with standards.
-
Goals: Identify and resolve design flaws early, streamline the validation process, and minimize post-production errors.
-
Pain Points: Limited early feedback on design quality, time-intensive validation checks, and difficulty predicting design flaws in complex models.
-
Motivations: Tim values AI tools that can predict potential quality issues, highlight areas of risk in models, and provide support in the validation process. He’s particularly interested in tools that integrate with CAD to flag issues before the prototype phase.
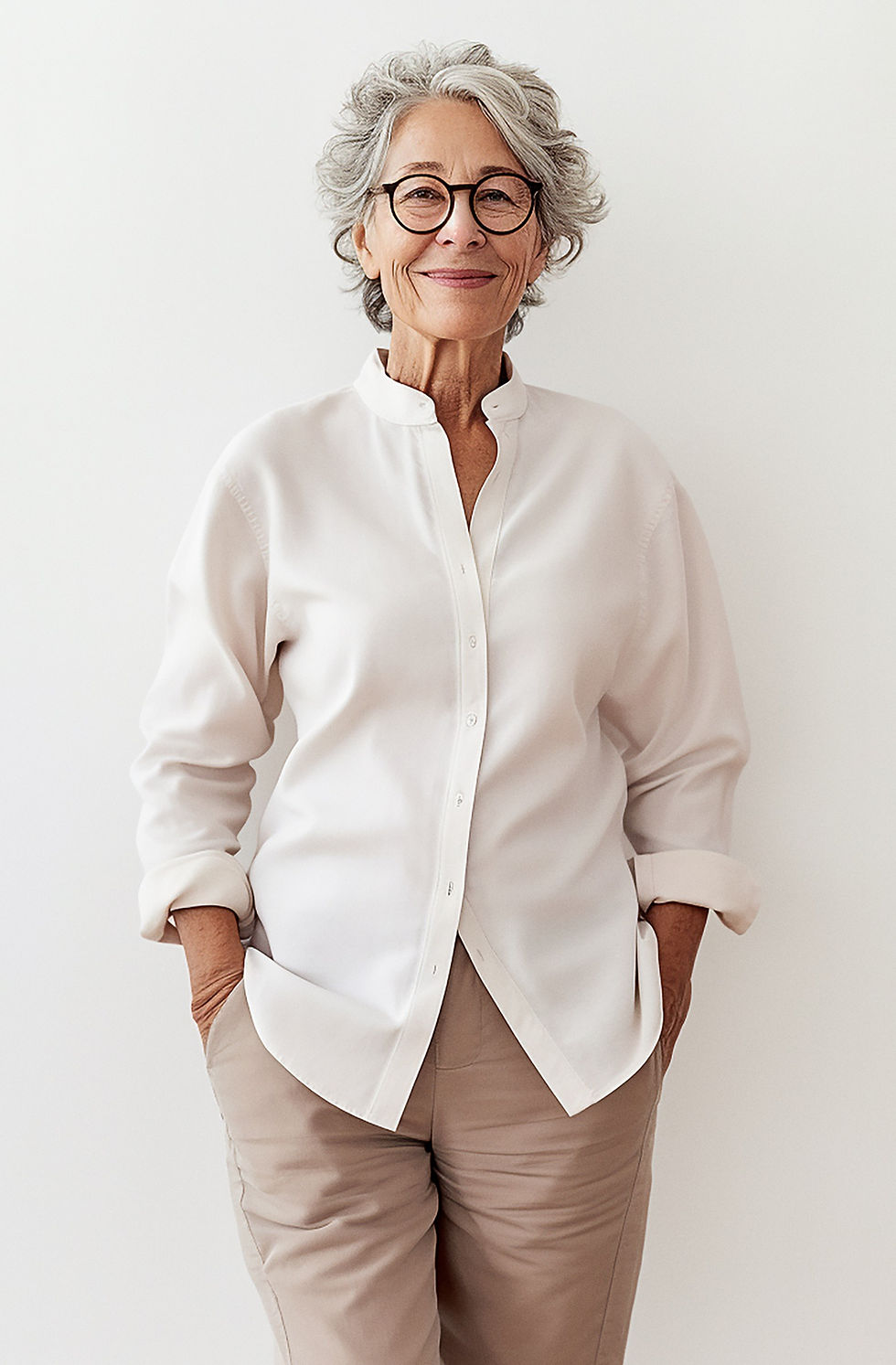

Priya - Product Manager
Type C
Oversees the Planning and Prototype Phases
Priya has 8 years of experience managing cross-functional teams in manufacturing, bridging design, engineering, and production. She’s familiar with CAD but mainly in a supervisory capacity.
-
Goals: Keep projects on track, ensure team alignment, and manage stakeholder expectations while balancing quality and timelines.
-
Pain Points: Coordinating between departments, limited insight into design progress, and handling delays from feedback cycles and rework.
-
Motivations: Priya values transparency in the design process and is interested in tools that improve collaboration, track project progress, and provide actionable insights. She sees AI as a means to improve communication and predict project bottlenecks.
#Observation 1
Most users spent a significant amount of time inspecting the model to understand the details from different perspectives.
This was identified as a low point in the journey map due to several challenges:
-
Users struggled to decide on the variations of drawings needed to capture the required details based on manufacturer specifications.
-
Concerns were raised about managing revisions effectively.
-
Last-minute changes added to users' frustrations and uncertainty.
Scenario
A participant unintentionally excluded a sectional view required for manufacturing, which was later flagged during cross-validation.

#Observation 2
A significant challenge was users relying on trial and error to determine the scale and manually positioning the drawing on the sheet.
This was identified as a low point in the journey map due to several challenges:
-
Determining the scale and size of drawing views depends on the level of detail to be captured and custom inputs.
-
Users must apply critical thinking to decide on drawing view scales and sheet sizes, a process identified as suitable for automation using AI/ML logic.
Scenario
A participant pointed out that "Smaller details often overlap or get lost in cluttered drawings."
Another participant remarked, "I’m never sure if this sheet size is correct for what the vendor needs."
#Observation 3
Adding dimensions and annotations to the drawings was a high cognitive load task—tiring, repetitive, yet essential—leaving users largely dissatisfied.
This was identified as a low point in the journey map due to several challenges:
-
Many users noted, "Tasks like dimensioning and annotating are time-consuming and demand close attention to detail; AI could assist us with this."
Scenario
Participants frequently stated they wished for "Automatic placement of dimensions for standard features."
"It takes too long to incorporate feedback because the process isn’t integrated into the tool," one participant explained."


Define/CX Journey Mapping
Determining if AI/ML adds value
Change is always a challenge, especially for long-time users who’ve been with the product since it first launched in the early 2000s. We wanted to introduce AI/ML workflows that not only bring value to everyone but also feel like a natural, easy-to-accept improvement.
We aimed to visualize the customer journey with a focus on the manufacturing sector.
The objective of the Customer Experience (CX) journey map was to align all cross-functional teams on a shared understanding of user pain points and identify potential opportunities.
Define/Takeaways
Opportunities Emerged
Through CXJ mapping and validation sessions, several pain points and opportunities were uncovered.
My focus was on the detailed design and drawing creation phase, a critical step in CAD modeling that serves as the MVP of the process. This phase provides essential production references for stakeholders like resellers and vendors.
"Basic drawings don't take much time; it's the details that are time-consuming."
- Participant quote

3DEXPERIENCE World 2024 | Dallas, Texas, USA
They questioned whether AI would rely on local datasets and raised concerns about small businesses struggling to train AI systems without large datasets.
Data Sourcing for AI
Users were concerned about whether AI could document design processes effectively, explaining changes such as why Design A was updated to Design B.
AI-Assisted Documentation
While basic drawings are quick to produce, users emphasised that detailing tasks, like dimensioning, are time-consuming and sought AI assistance to speed up these processes.
Efficiency in Detailing
There was a strong interest in AI helping to read and interpret 2D data from sheets to improve workflow efficiency.
2D Data Interpretation
Discover/User Research
Qualitative
Focus Group Session
We conducted focus group interviews to explore user expectations for AI/ML, such as enhanced efficiency, and to address concerns around trust and control. The feedback on features like proactive suggestions played a key role in shaping user-centric design strategies.
Each session lasted about an hour, during which participants shared their thoughts, expectations, and concerns regarding AI/ML. Below are some common topics that emerged.


1
Drawing View Selection
Selecting drawing views manually violates efficiency principles and increases the likelihood of errors, affecting task performance and consistency.
Mapped Heuristics:
-
Efficiency of Use: Manual selection of views for complex models is tedious and time-consuming.
-
Error Prevention: Critical views or dimensions are often missed due to the manual process.
-
Consistency and Standards: Variability in view selection between users disrupts project uniformity.
2
Drawing Sheet Parameters
Difficulty in setting sheet parameters disrupts clarity and leads to suboptimal outputs, impacting usability and task efficiency.
Mapped Heuristics:
-
Match Between System and the Real World: Novices struggle to align parameters with real-world requirements.
-
Aesthetic and Minimalist Design: Overcrowded or unclear sheets reduce readability.
-
Flexibility and Efficiency of Use: Lack of predefined standards increases the setup time for new projects.
3
Dimension and Annotations
Dimensioning and annotations impose a high cognitive load and lack automation, leading to slower workflows and reduced accuracy.
Mapped Heuristics:
-
Recognition Rather Than Recall: Users manually recall which dimensions or annotations to add, increasing cognitive effort.
-
Flexibility and Efficiency of Use: Repetitive tasks remain unoptimized, wasting time.
-
Help Users Recognize, Diagnose, and Recover from Errors: Feedback mechanisms for validation and corrections are insufficient.
My Learnings
I learned to appreciate the varying needs of novice and expert users, applying heuristic principles to enhance the user experience. Collaboration with engineers and stakeholders was crucial, as was the iterative design process, which relied heavily on continuous user feedback.
AI in CAD
Leveraging AI to reduce cognitive load and automate tasks proved to be a significant enhancement.
Migrating from Legacy Systems
Describe the item here. Include important features, pricing and other relevant info.
Adapting UX Principles to Niche Domains
Applying heuristic principles such as error prevention and consistency in a CAD context proved essential. I identified that manual view selection violated consistency principles, leading to the proposal of AI solutions for standardization.
